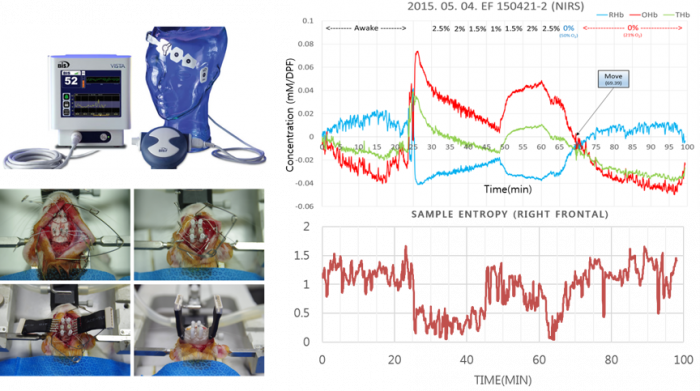
Currently, EEG and NIRS are common techniques to investigate brain functional activities due to their low cost, high temporal resolution, and portability. EEG provides brain activity information directly through electrical signal, while NIRS measures brain activity indirectly through hemodynamic response. In our lab, in order to complement information on hemodynamic responses of NIRS to EEG, we utilized a combined EEG/NIRS system to monitor anesthesia depth.
EEG electrode and NIRS optodes were surgically inserted to rat's brain to monitor anesthesia depth (Dong-Hyuk Choi, Seonghyun Kim, and Jaeyoung Bae)
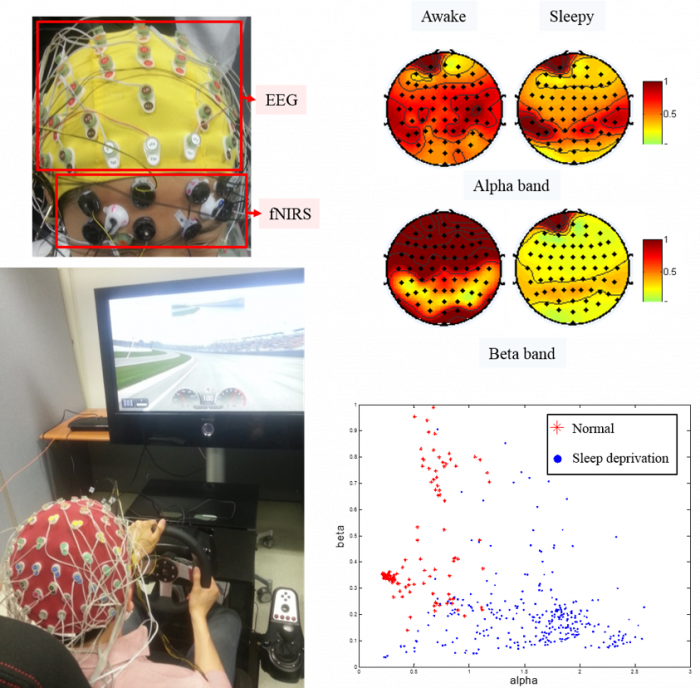
In addition, combined EEG/NIRS system was noninvasively applied to human to detect driver drowsiness.
Combined EEG/NIRS in driver drowsiness detection study (Thien Nguyen et al.)